How to enable Security settings in ABA Matrix
This guide is essential for anyone looking to enhance their security within the ABA Matrix system. It details the implementation of critical features like Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and a Password Expiration Policy, which significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. By following the steps outlined, users can customize their security settings to balance ease of use with robust protection. Ultimately, this guide empowers users to safeguard their accounts more effectively while maintaining a user-friendly experience.
Security features:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Password Expiration Policy.
Security settings
1. To enable these settings, just go to Agency

2. Go to Settings

3. Go to the "Security" settings
Email Two-Factor Authentication
Email Two-Factor Authentication provides an additional layer of security beyond passwords. When the user logs in, an authorization code is sent to their email. The user must then enter this code to access their account
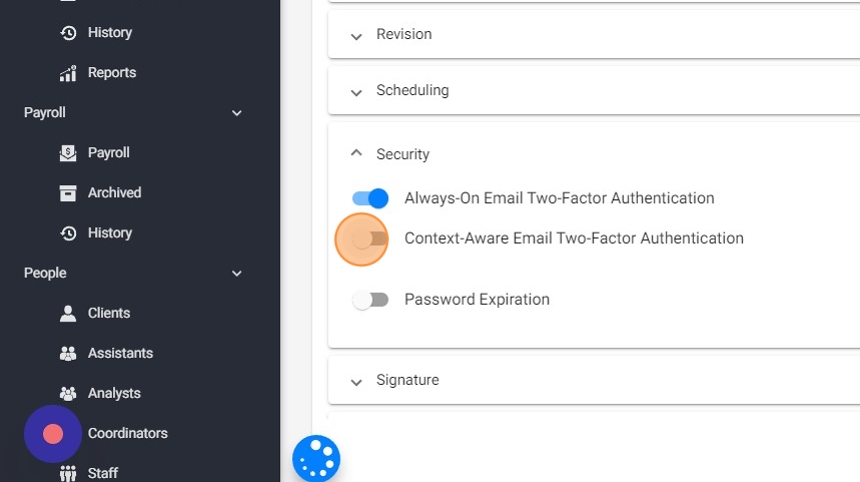
4. Context-Aware Email Two-Factor Authentication:
If you enable this setting, the two-factor authentication is required only when specific contextual factors change, like logging in from an unfamiliar device, browser, or IP address. Context-aware two factor authentication provides a substantial increase in the account's security, while being less invasive and more user friendly than the Always-on two factor authentication.
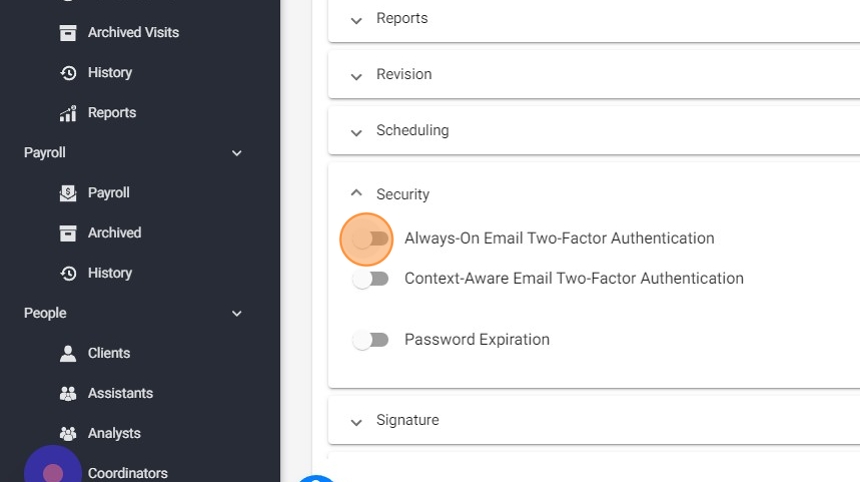
5. Always-On Email Two-Factor Authentication:
If you enable this setting, the two-factor authentication is required every time an user logs in. While being more secure than the context-aware two factor authentication, it can create significant friction for the user experience.
Password expiration
The primary goal of password expiration is to mitigate the risk associated with compromised passwords by ensuring that passwords are changed frequently, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access to user accounts.
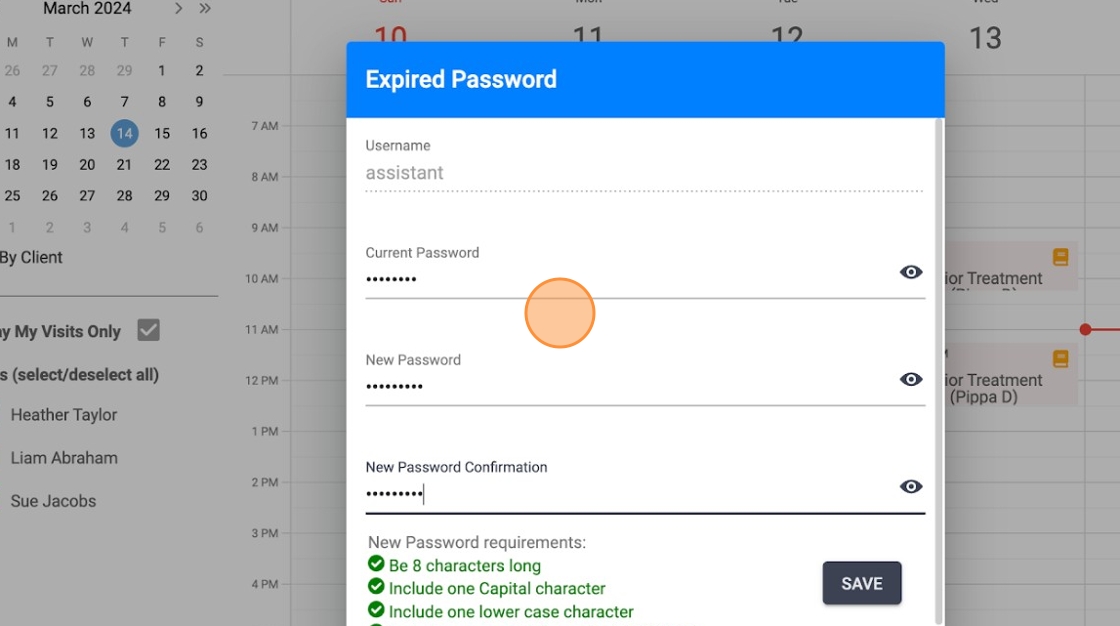
6. Password expiration:
If you enable this setting, users will have to regularly change their passwords at predefined intervals.

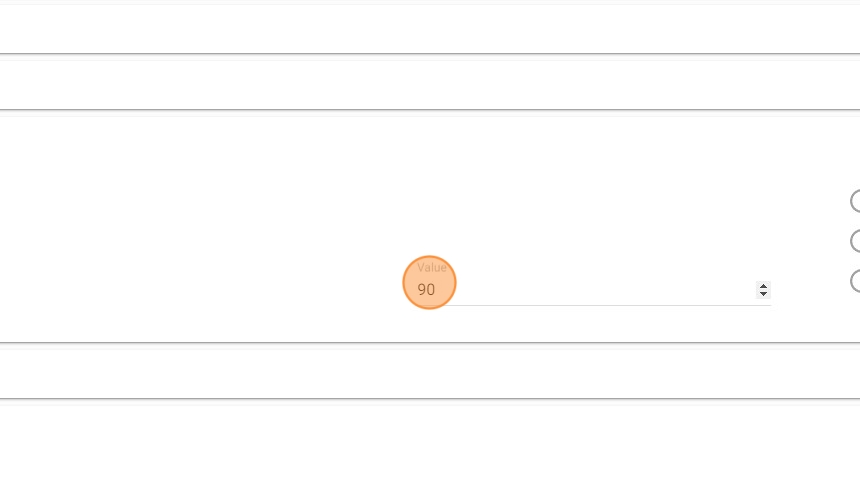
7. In the "Value" field you can set the number of days to indicate how long users have before they must change their passwords following a password modification, usually every 30, 60, or 90 days.
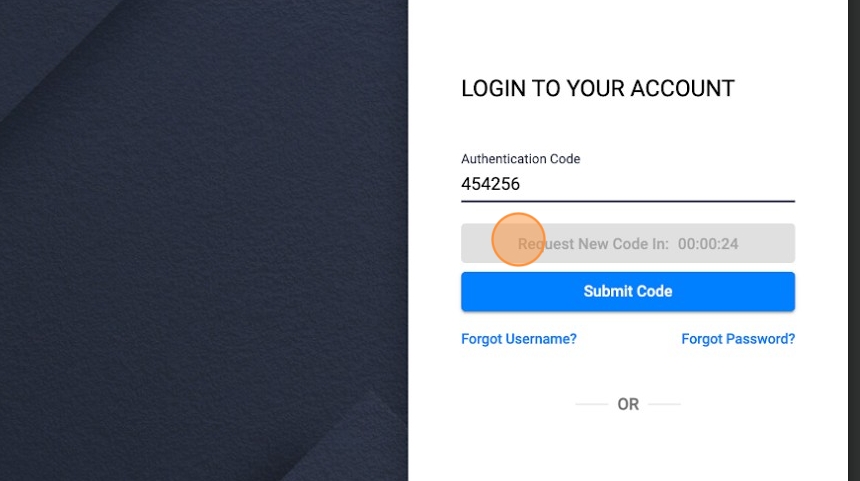
How the Email Two-Factor Authentication works:
8. Login Attempt: When a user tries to log in to the system, they first enter their username and password as usual.

9. Email Code Generation: Upon successful entry of the username and password, the system generates a unique one-time authentication code.
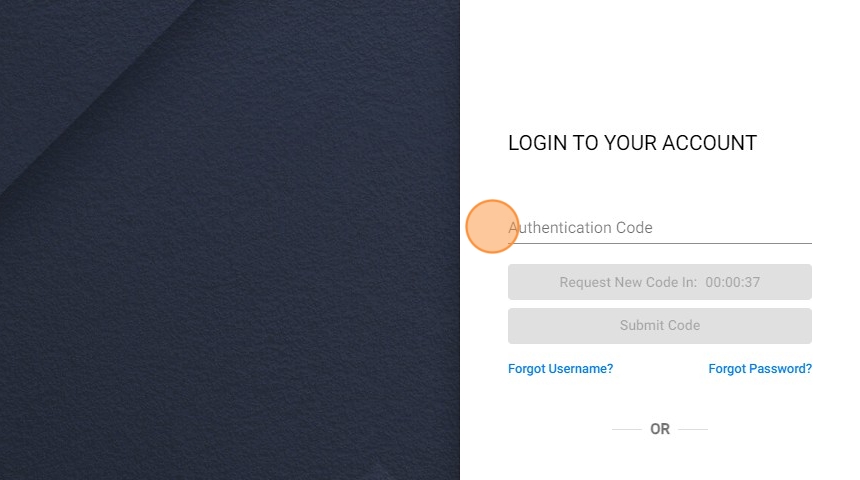
10. Code Delivery via Email: The system sends this authentication code to the user's registered email address in real-time. The user needs to check their email inbox for the authentication code, and once received, they have to enter this code into the login interface within a specified time frame (30 minutes).
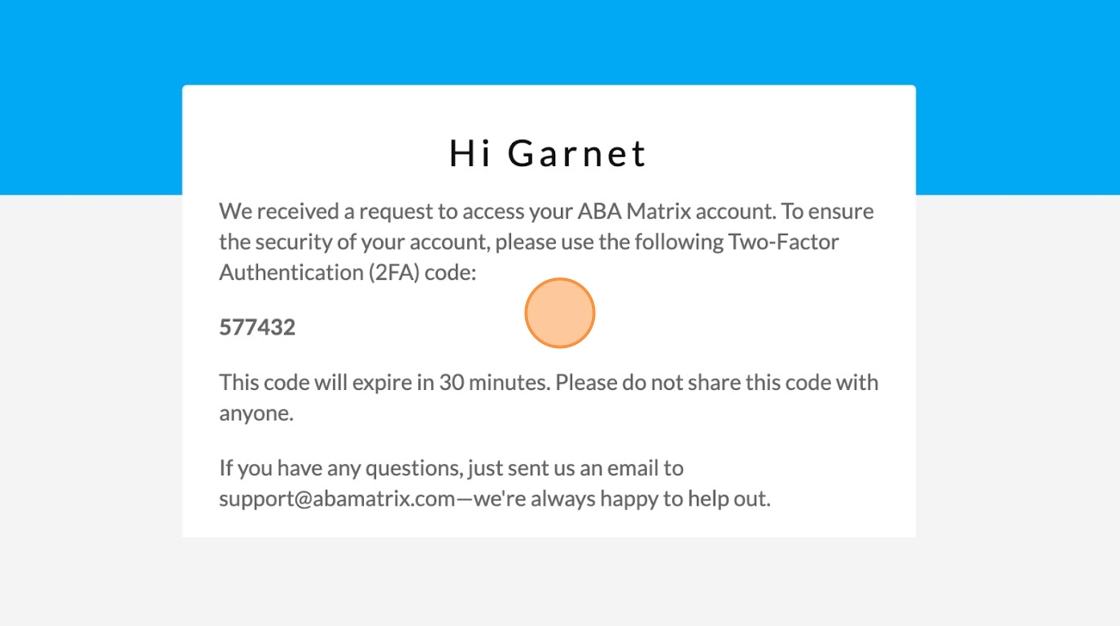
11. Code Verification: The system verifies that the code entered by the user matches the one that was generated and sent via email. If the codes match and are within the valid time window, access to the system is granted.
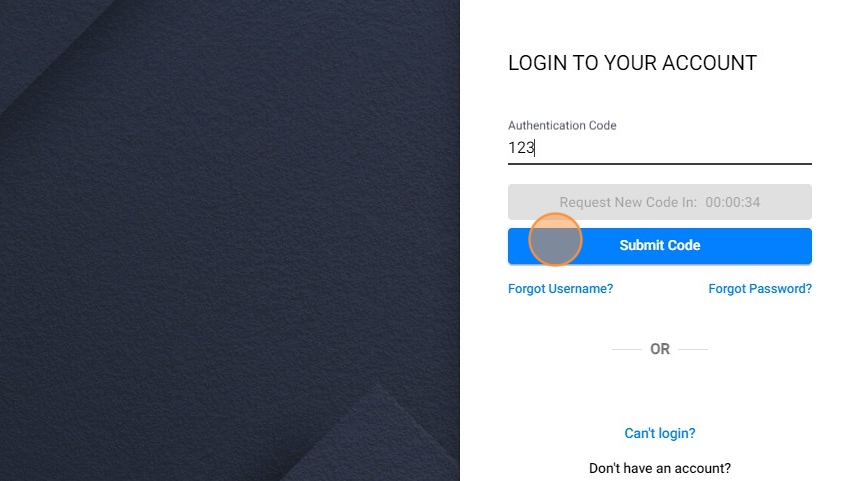
12. How to Request a New Code: If the user did not receive the email containing the verification code, or if the code has expired, they can request a new one through the system's interface. After a certain period of time they will be able to select this option. Then the system sends the transmission of another email containing a new verification code to be sent to the user's registered email address.
How the password expiration works:
13. Password Change Requirement: Upon successful login, users are required to periodically change their passwords based on the agency's settings. When the predetermined time arrives, users are prompted to generate a new password that complies with specified criteria. Upon successful creation, users maintain access to the system with the newly updated password.