How to change measures, status, functions or topography (for analysts)
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to change measures, status, functions, or topography in an existing maladaptive behavior. It is applicable not only to maladaptive behaviors but also to replacement behaviors, skill acquisitions, caregiver goals, and RBT goals. The guide includes clear instructions and images to help users easily navigate the process.
For the purpose of this tutorial, only Maladaptive Behaviors will be explained, but it will work the same for Replacement Behaviors, Skill Acquisitions, Caregiver Goals and RBT Goals.
1. How to change Measures
1. Click the Maladaptive Behavior to be modified to open the info panel.
Once the info panel is open, select the Measures tab:

2. Click on the "Change Measures" button (see image):

3. Select the new Measure and click on "Save".

4. Note that the effective date when these changes are going to be applied to the system can also be modified

1.1. Types of measurements
1.1.1. Frequency
Frequency: This is the number of times the behavior occurs. You measure the frequency of a behavior simply by counting each time it happens.
5. To collect data on frequency, you should add the number of occurrences.
You can add and subtract occurrences using the "+" and "-" symbols, or type the number directly.

1.1.2. Percentage
Percentage: This is a measurement that shows the proportion of a behavior in relation to the total number of opportunities or responses. It is calculated by dividing the number of specific responses by the total number of responses or opportunities, then multiplying by 100 to obtain the result as a percentage.
6. To collect data as a percentage, you should first add the number of attempts, and then define which of those attempts were successful or not.
- The number of attempts is added in the same way as occurrences.
- To define whether an attempt was successful (YES) or not (NO), simply click on the attempt, and it will toggle between YES and NO.

1.1.3. Intervals
Intervals: Interval recording is a technique used to collect data by dividing the observation period into a specific number of intervals. During each interval, it is recorded whether the behavior occurred or not. At the end, the percentage of intervals in which the behavior occurred is calculated.
7. To collect data in intervals, you should first add the number of intervals, and then define in which ones the behavior occurred or not, similar to percentage.
- The number of intervals is added in the same way as attempts.
- To define whether the behavior occurred (YES) or not (NO) in a particular interval, simply click on the interval, and it will toggle between YES and NO.

1.1.4. Intensity
Intensity measurement for behaviors refers to quantifying the strength or magnitude of a behavior. This type of measurement captures how powerful or forceful a behavior is, rather than just how often it occurs.
8. To collect data on intensity, you must first add the interval, and then define the intensity of each one.
- The number of intervals is added in the same way as attempts.
- To define the intensity of the interval, simply click on the interval until it reaches the correct intensity.

1.1.5. Time -seconds- / Time -minutes- / Time (sum) -min-
Data collection for behavior in terms of time measurement involves recording behavioral occurrences within specific time frames. Regardless of the method used, time-based data collection allows for the analysis of behavior patterns, identification of trends, and evaluation of interventions' effectiveness over time.
- Time -seconds- : This measure records the duration in seconds. It is useful for precise measurement of short-duration behaviors.
Example: if a behavior occurs 5 times with durations of 10s, 12s, 8s, 15s and 11s, the average duration is (10 + 12 + 8 + 15 + 11) / 5 = 11.2 seconds.
- Time -minutes-: the duration is recorded in minutes and the average duration is calculated.
Example: if a behavior occurs 3 times with durations of 5, 7 and 6 minutes, the average duration is (5 + 7 + 6) / 3 = 6 minutes.
- Time (sum) -min-: Measures the total accumulated duration of a behavior in minutes across multiple instances throughout the session.
Example: if a behavior occurs with durations of 10 , 15 and 20 minutes over a session, the total time is 10 + 15 + 20 = 45 minutes.
9. To collect data in time, whether in seconds or minutes, you should first add the number of occurrences, and then define the time for each of those occurrences.
- The number of occurrences is added in the same way.
- To define the time for each occurrence, you can use the symbol or enter it manually.

1.1.6. Task Analysis
Task analysis, as a measurement tool in behavior analysis, involves breaking down complex tasks or behaviors into smaller, more manageable steps. These steps are then measured to assess an individual's performance or progress in completing the task. By quantifying the completion of each step, task analysis allows for the objective measurement of behavior and provides valuable data for evaluating skill acquisition or task mastery over time.
10. To collect data using task analysis, you will have the steps previously established in the client's profile available, and you only need to select the prompt level for each task.

1.1.7. Rate -hours
Rate-hours measurement in behavior analysis involves tracking the frequency of behavior occurrences over a specific period of time, typically in hours. This measurement method allows for the calculation of the rate at which a behavior occurs per hour.
11. To collect data in rate according to the hours of visit duration, you only need to collect the number of occurrences during the session. In this case, the rate will be calculated based on the number of incidences over the duration of the session.

1.2. Additional Features in Measures: Baseline and Initial Observations
12. Baselines can be added for the selected measure (as shown in image below):

13. You can also add initial observations. These are observations conducted before the baseline process, mostly by the analyst of the case.

1.3. Non-Active Measures
14. Notice Non-Active Measures can be deleted:

If you delete the previous measurement, you can use the new measurement starting from the same effective date. The data will transfer only if the new and old measurements are compatible; otherwise, the data will be lost.
2. How to change Status
15. Click the Maladaptive Behavior to be modified to open the info panel.
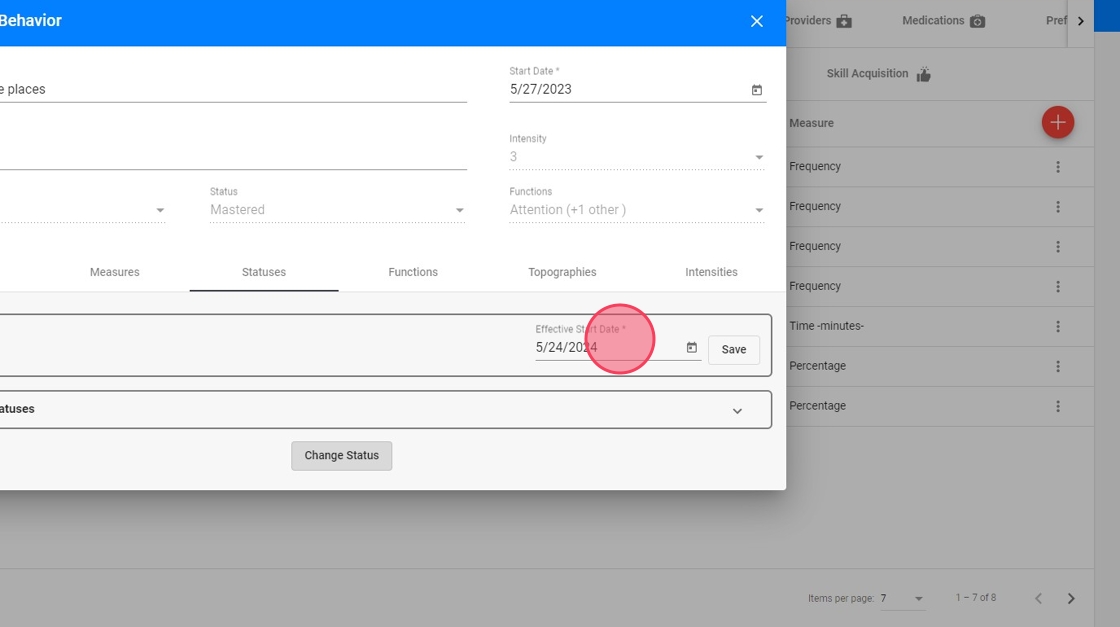
Once the info panel is open select the Statuses tab and click on the "Change Status" button (see image)

16. Select the new Status and click on "Save":

The available statuses within the system include:
- In Observation: This status is assigned to behaviors when they are newly observed. Data collection is allowed.
- This status is available only at the beginning of the behavior observation.
- Pending: Behaviors marked as "Pending" do not require data collection. They are typically used for behaviors that are not currently being addressed or are awaiting further action.
- Ongoing: Behaviors categorized as "Ongoing" require regular data collection. These are behaviors that are actively being targeted and monitored for progress..
- Mastered: Behaviors in the "Mastered" status indicate that the behavior has been successfully addressed and no longer requires data collection. They are not displayed in the session notes.
- Discontinued: Behaviors labeled as "Discontinued" are no longer being targeted or addressed. They do not require data collection and are not displayed in the session notes.
Understanding these behavior statuses and their associated data collection procedures is essential for effectively managing and tracking behavior progress in our system.
17. Note that the effective date when these changes are going to be applied to the system can also be modified (as shown in image below):
3. How to change Functions (Maladaptive Behaviors only)
18. Click the Maladaptive Behavior to be modified to open the info panel.
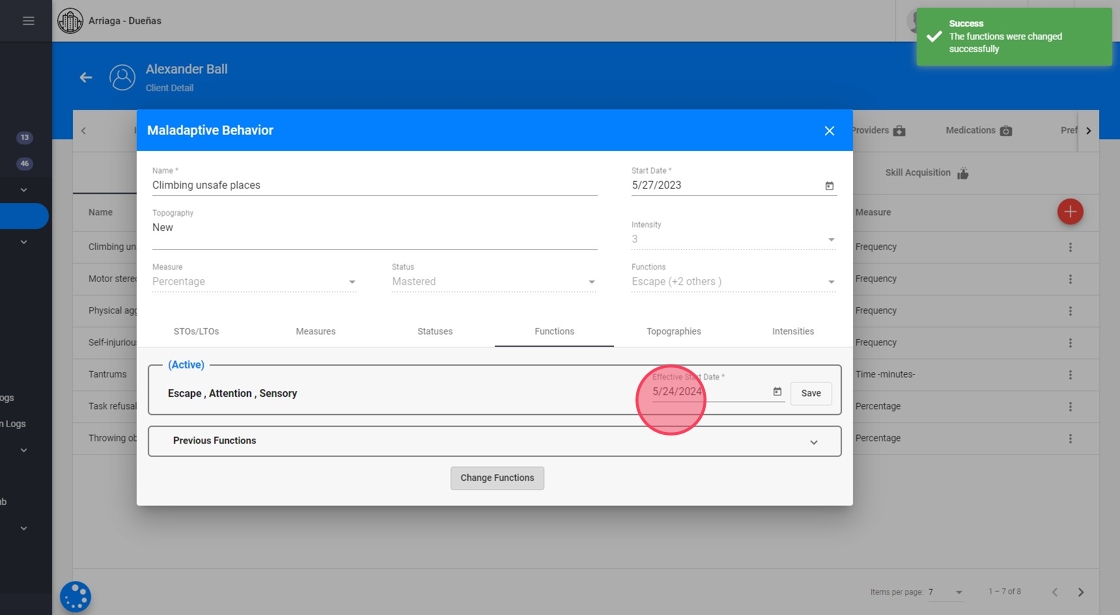
Once the info panel is open select the Functions tab and click on the "Change Functions" button (see image):

19. Select the new Function(s) and click on "Save":

20. Note that the effective date when these changes are going to be applied to the system can also be modified (as shown in image below):
21. Notice non-Active Functions can be deleted:

4. How to change Topography
22. Click the Maladaptive Behavior to be modified to open the info panel.
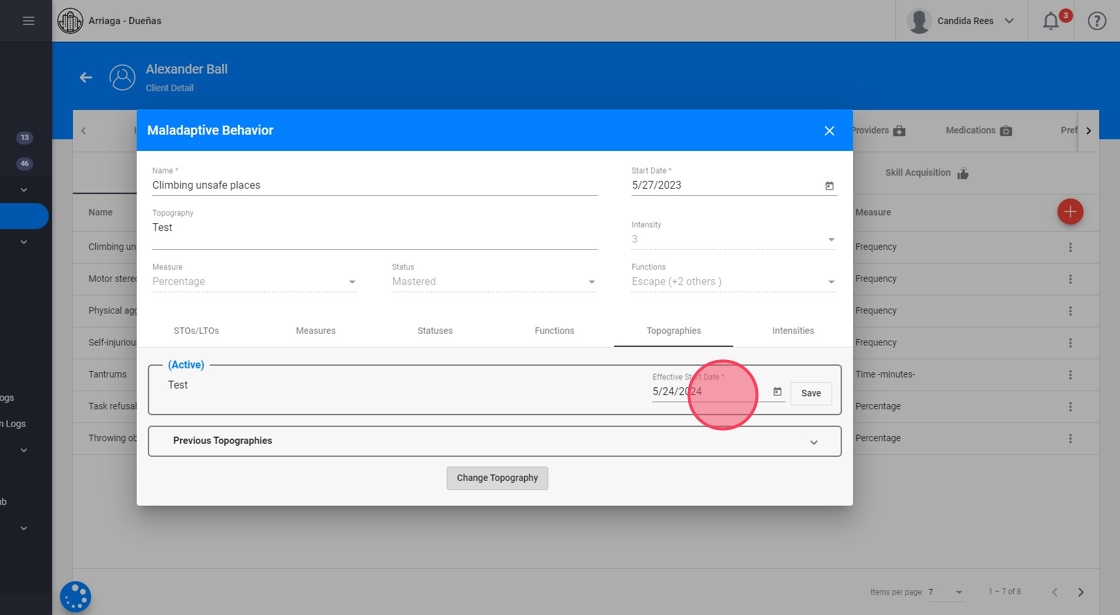
Once the info panel is open, select the Topographies tab and click on the "Change Topography" button. Type the new Topography and click on "Save" (see image):

23. Note that the effective date when these changes are going to be applied to the system can also be modified (as shown in image below):
24. Notice non-Active can be deleted:

